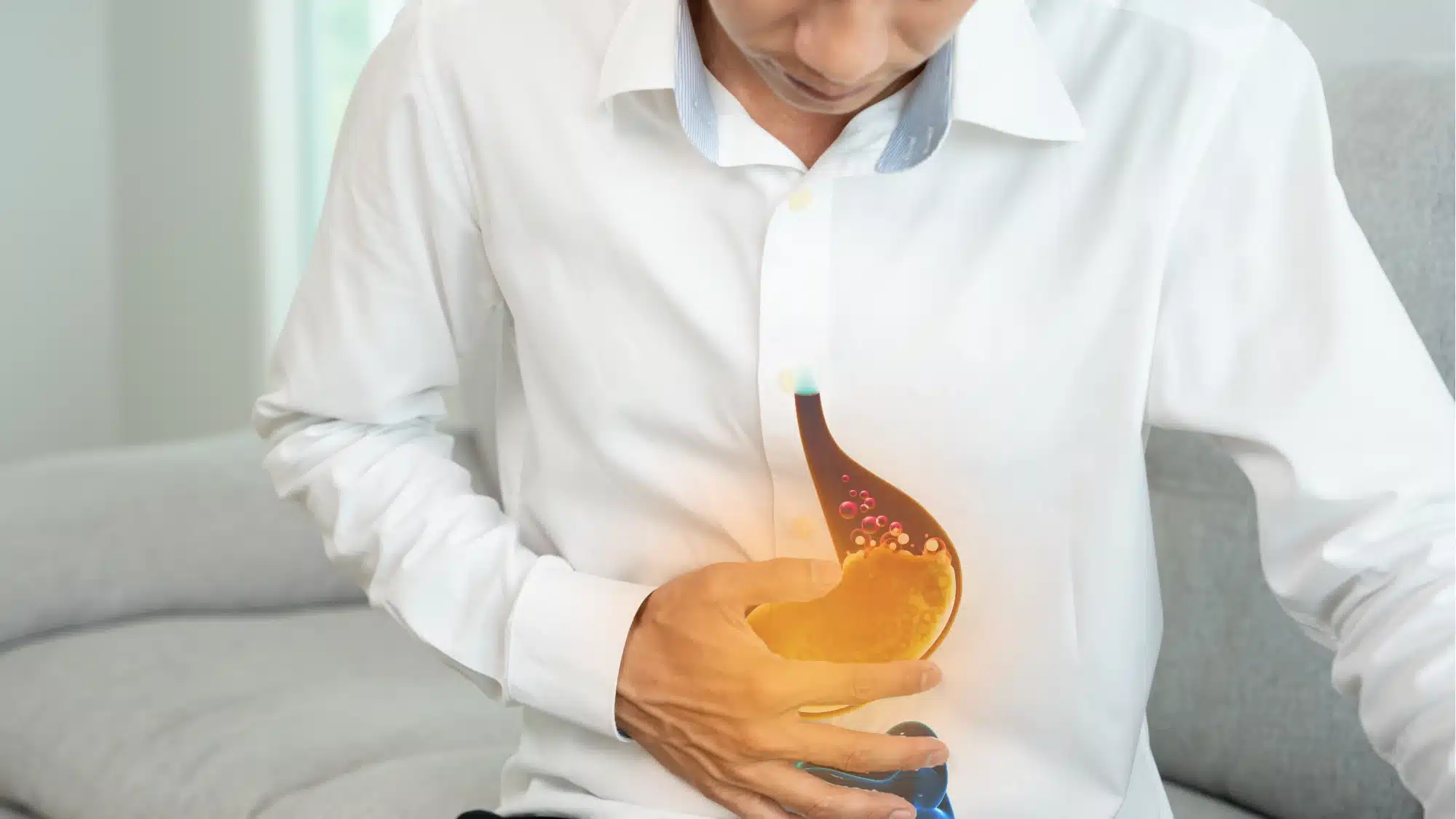
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common yet often misunderstood condition that affects the digestive system. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and risk factors associated with GERD is crucial for managing and preventing its effects. At Merus Gastro, your trusted gastroenterology clinic in Suwanee, GA, we are dedicated to providing comprehensive care and information to help you navigate GERD effectively.
What is GERD?
GERD is a chronic condition where stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, the tube connecting your mouth and stomach. This backflow of acid, known as acid reflux, can irritate the lining of the esophagus and lead to various symptoms and complications.
Symptoms of GERD
GERD can manifest in a variety of ways, some more common than others. Recognizing these symptoms can help in seeking timely medical advice and treatment.
- Heartburn
- Description: A burning sensation in the chest, often after eating, which may worsen at night.
- Frequency: Occurs frequently and can be severe, disrupting daily activities.
- Regurgitation
- Description: A sour or bitter-tasting acid backing up into your throat or mouth.
- Impact: Can lead to discomfort and bad breath.
- Dysphagia
- Description: Difficulty swallowing or a feeling of food being stuck in the throat.
- Consequences: Can lead to nutritional deficiencies and weight loss if persistent.
- Chest Pain
- Description: Pain or discomfort in the chest, which can sometimes be severe.
- Differentiation: Important to differentiate from heart-related pain; medical evaluation is essential.
- Chronic Cough and Laryngitis
- Description: Persistent cough or inflammation of the voice box causing hoarseness.
- Link: Often mistaken for respiratory issues but linked to acid reflux.
- Asthma Symptoms
- Description: GERD can worsen asthma or mimic asthma symptoms.
- Mechanism: Acid entering the esophagus can cause spasms in the airways.
Causes of GERD
Several factors contribute to the development of GERD. Understanding these can aid in managing and potentially reducing symptoms.
- Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES) Dysfunction
- Function: The LES acts as a valve between the esophagus and the stomach.
- Issue: If the LES weakens or relaxes abnormally, stomach acid can flow back into the esophagus.
- Hiatal Hernia
- Condition: Occurs when the upper part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity.
- Impact: Disrupts the normal function of the LES.
- Obesity
- Pressure: Excess body weight puts pressure on the abdomen, pushing up the stomach and causing acid reflux.
- Prevalence: Higher incidence of GERD in overweight or obese individuals.
- Pregnancy
- Changes: Hormonal changes and increased abdominal pressure during pregnancy can lead to GERD.
- Management: Often resolves after childbirth, but requires management during pregnancy.
- Diet and Lifestyle
- Trigger Foods: Spicy foods, fatty foods, chocolate, caffeine, and alcohol can trigger acid reflux.
- Habits: Eating large meals, lying down after eating, and smoking can exacerbate GERD symptoms.
Risk Factors for GERD
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing GERD. Being aware of these can help in prevention and early intervention.
- Age
- Trend: GERD can occur at any age but is more common in adults over 40.
- Management: Age-related weakening of the LES can increase risk.
- Genetic Predisposition
- Family History: A family history of GERD increases the risk of developing the condition.
- Research: Studies suggest a genetic component to GERD.
- Lifestyle Choices
- Smoking: Smoking weakens the LES and increases acid production.
- Alcohol Consumption: Alcohol can relax the LES and irritate the esophagus.
- Medications
- Impact: Certain medications, such as antihistamines, calcium channel blockers, and antidepressants, can relax the LES and exacerbate GERD symptoms.
- Consultation: Discuss medication use with your healthcare provider if experiencing GERD symptoms.
- Eating Habits
- Patterns: Eating large meals or eating close to bedtime can trigger acid reflux.
- Diet: A diet high in fatty and spicy foods increases the risk of GERD.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you experience frequent or severe symptoms of GERD, it’s important to consult a gastroenterologist. Persistent GERD can lead to complications such as esophagitis, esophageal stricture, Barrett’s esophagus, and an increased risk of esophageal cancer.
At Merus Gastro, we provide expert care for GERD and other digestive conditions. Our team in Suwanee, GA, is equipped with the knowledge and tools to diagnose and manage GERD effectively, ensuring you receive the best possible care.
Conclusion
GERD is a common condition that can significantly impact your quality of life. By understanding its symptoms, causes, and risk factors, you can take proactive steps to manage and prevent its effects. At Merus Gastro, we are committed to helping you achieve better digestive health through comprehensive care and personalized treatment plans.
Contact Us
If you’re experiencing symptoms of GERD, don’t wait to seek help. Contact Merus Gastro today to schedule a consultation with our experienced gastroenterologists in Suwanee, GA. Let us help you take control of your digestive health and improve your quality of life.